 |
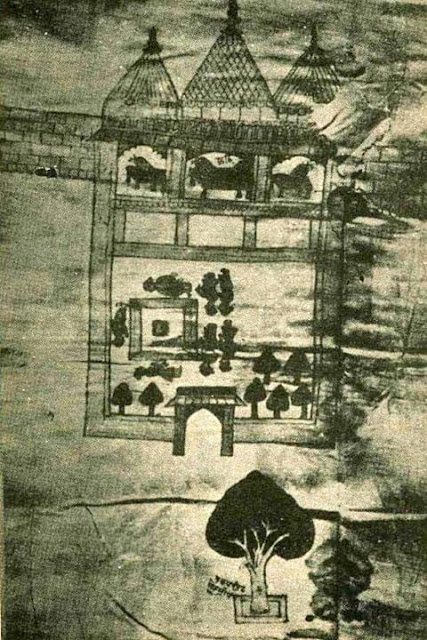
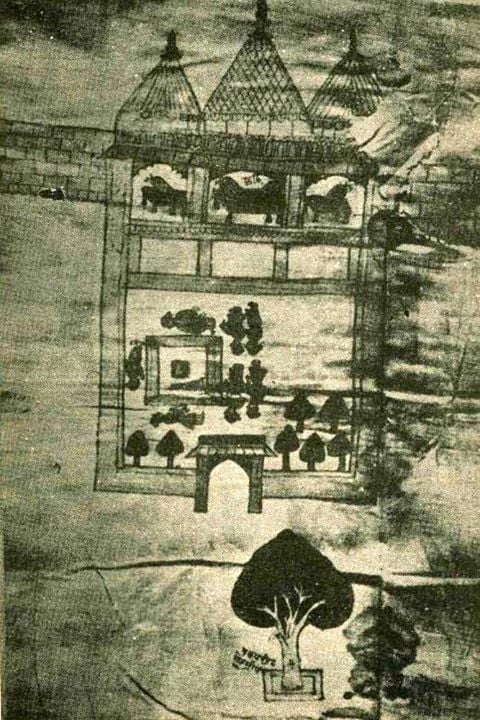
| The earliest map of Ram Janmasthan at Ayodhya (1717 CE) |
The earliest record of a mosque at the site traditionally believed by Hindus to be the birthplace of Rama comes from Jai Singh II (or "Sawai Jai Singh") a Rajput noble in the Mughal court who purchased land and established a Jaisinghpura in the area surrounding the mosque in 1717 (as he had also done in several other Hindu religious places). The documents of Jai Singh preserved in the Kapad-Dwar collection in the City Palace Museum of Jaipur, including a sketch map of the Babri Masjid site. The map shows an open courtyard and a built structure with three temple spires (Sikharas) resembling today's Babri Masjid with three domes. The courtyard is labeled Janmasthan and shows a Ram Chabutra. The central bay of the built structure is labeled Chhathi, which also denotes birthplace.
Professor R. Nath, who has examined these records, concludes that Jai Singh had acquired the land of Rama Janmasthan in 1717. The ownership of the land was vested in the deity. The hereditary title of the ownership was recognized and enforced by the Mughal State from 1717. He also found a letter from a Gumastha Trilokchand, dated 1723, stating that, while under the Muslim administration people had been prevented from taking a ritual bath in the Saryu river, the establishment of the Jaisinghpura has removed all impediment






![Central Museum Lahore - Annual Report (1935-1936) [Archaeological Survey of India]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEgIMS6YSjtiErbiSK_fZVVzWawfOW6KJtOIztqq7BxD2pgTimVZd5kYD8iUunJfUMq4Ken0u91UvBrBk-oDXZ9OkSmTX-fW9g1uRSpT-xHyZsFY1BCKgsqAbHoz0Hp9CObd73UB-_ix1YUa/w680/central-museum-lahore-annual-report-1935-1936.jpg)



0 Comments