Tiny CC's Custom Branded URL Shortening Guide
Uniform Resource Locaters are addresses used on the World Wide Web. Every web page or resource is specified by a unique URL, which means the internet consists of billions of URLs. They are the building blocks of navigation and the currency of the web. A hyperlink or link (clickable URL) is any text, image or button that you can click-on to jump to a new website or new page on the same site. There are only a few basic ways to access web pages:1) Click-on hyperlinks from another website.
2) Indirectly - find and click-on links from Google (or other search engine) results.
3) Directly - enter a domain or URL into a browser's address bar.
• Entering a domain or URL into the browser's web address field is known as direct navigation or "type-in" traffic and amounts to about 10% of internet traffic (a browser's address bar shows the current URL and will also accept a pasted-in or typed-in URL that the user wishes to go to).
• Social interface to the Web relies on email and networking sites. When users recommend web pages to each other, email and bookmarking sites are second only to search engines.
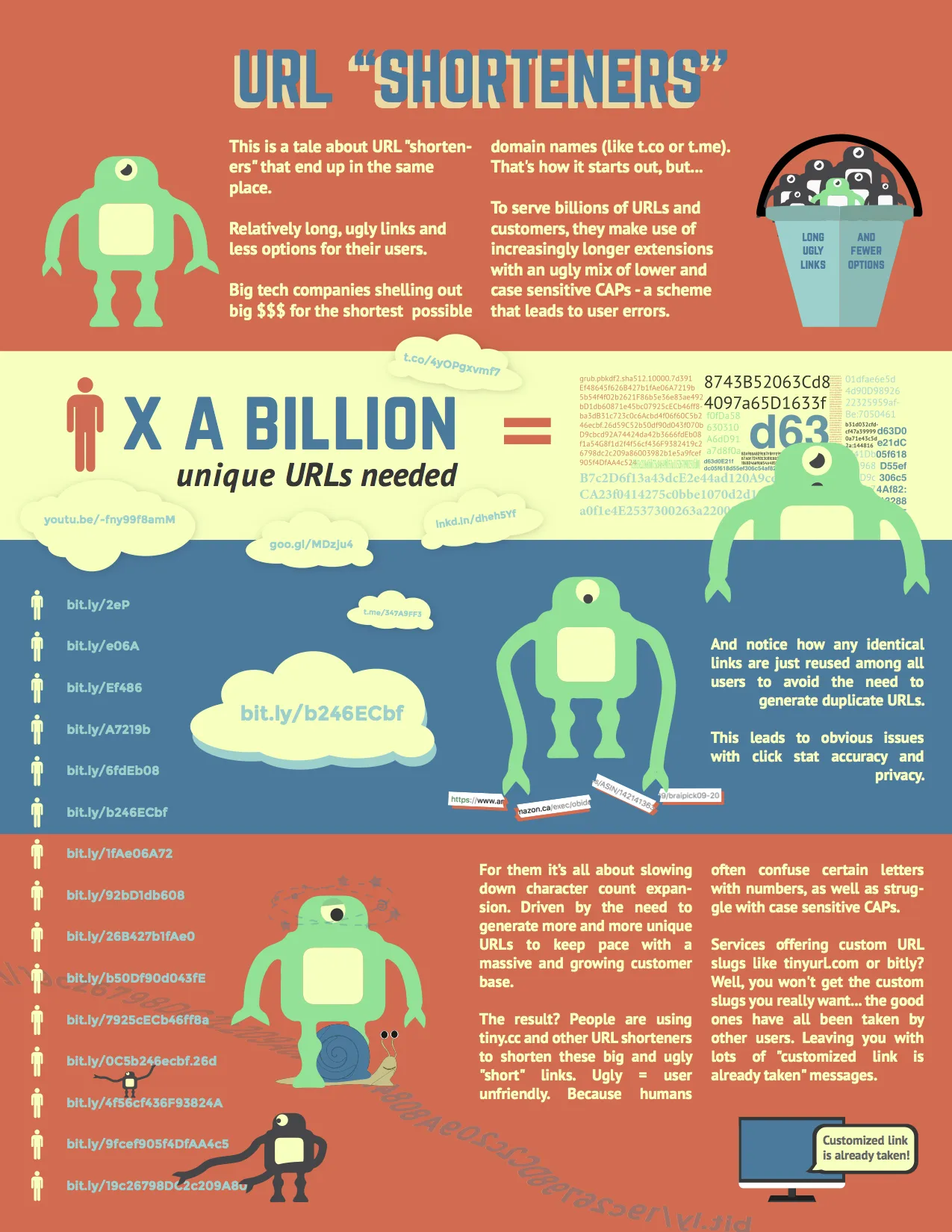
• URLs greater than 78 characters long will usually wrap across a line feed, increasing likelihood of breaking. Some email clients impose a length limit at which lines are automatically broken; requiring the user to paste a long URL back together, rather than just clicking on it. A short URL eliminates this problem.
• People sometimes guess the domain name of sites they have not visited before; so pick a name that describes your blog, company or brand. Even when people have been to a site before, they will often try to guess or remember the site name instead of using a bookmark or history list; so an ideal domain name is short, simple, memorable and easy to spell.
Create Custom Branded Short URLs with Tiny CC - Choose between Static and Dynamic URLs
• Static URLs get content directly from server files and always stay the same unless a webmaster purposefully changes an html file.• Dynamic URLs get content from templates + databases. When URLs are requested, a web script begins with a template and fills in details by fetching information from a database. Since database content can be subject to frequent updating that means webpage content can frequently change as well.
• The address itself will indicate static or dynamic. If it contains any query strings such as ? & = then it is a dynamic URL. eg: http://tiny.cc/newforum/thread.php?threadid= 357&sort=date (Note also that blank spaces are never allowed in a web address).
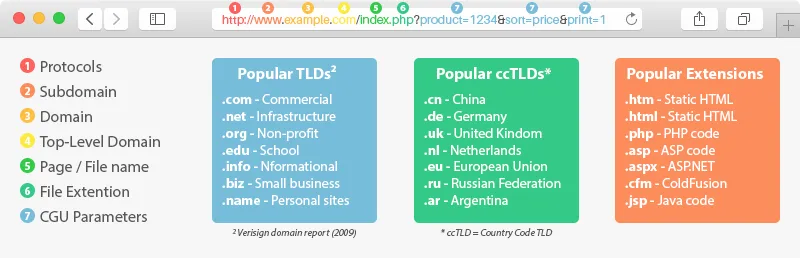
Static URLs only contain dots, slashes, dashes or underscores. eg: http://tiny.cc/newforum/url_discussion.html and are considered clean or user-friendly URLs because they are more human readable and descriptive than dynamic URLs. And static URLs are typically ranked better in search engine results while dyanmic URLs tend to not get indexed.
Parts of a URL

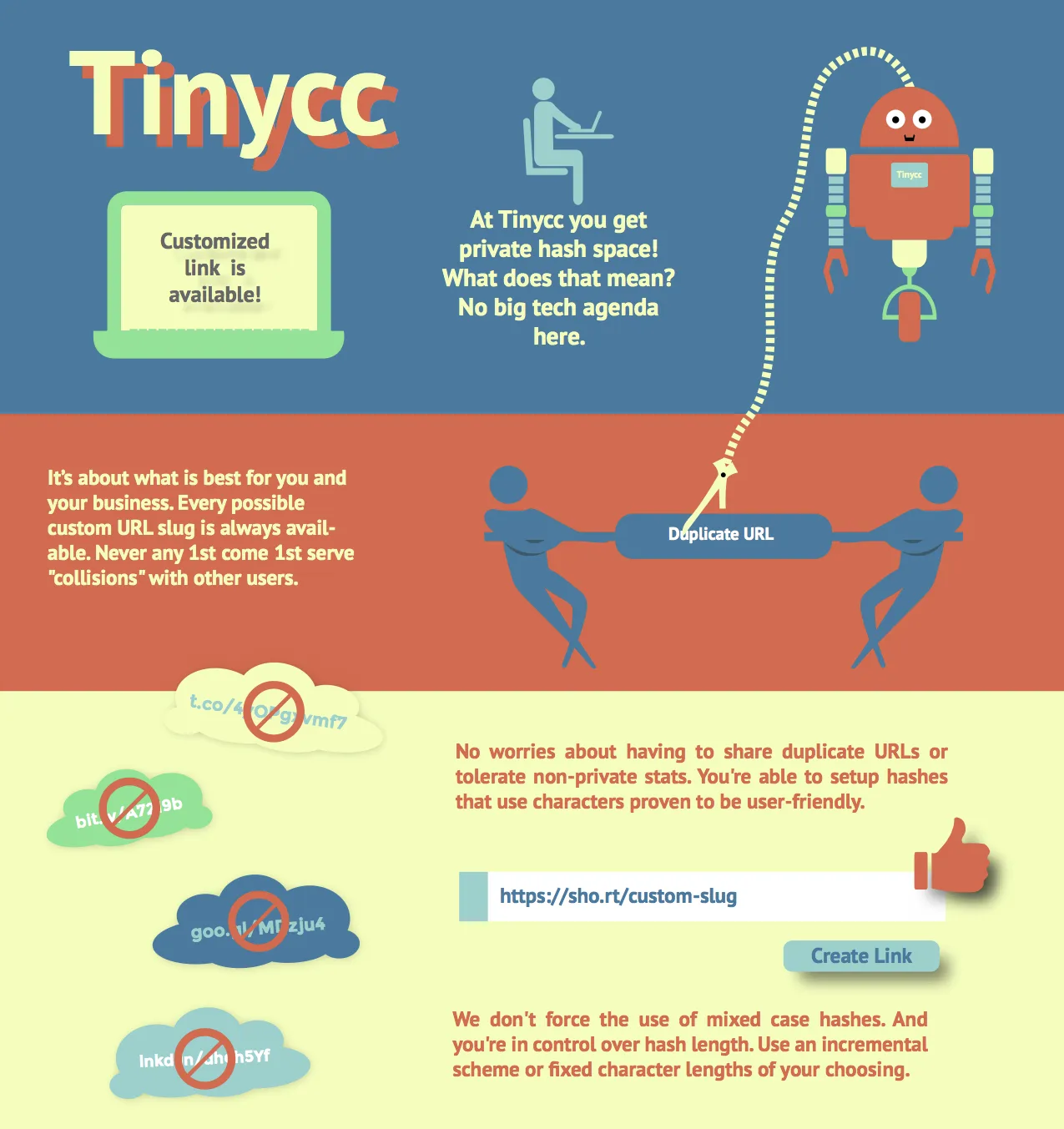
Note that www. is only a subdomain. Technically not part of any protocol, it is simply a convention standing for world wide web. In other words, www is arbitrary and no different than any other subdomain. This link example: www.tiny.cc/ contains an error due to the missing protocol. And http://www.tiny.cc is not a required format because the tiny.cc site happens to be configured without a subdomain (www. was made optional). http://tiny.cc is shorter and boiled down to only the required parts that make a URL functional: protocol + domain + top level domain (http:// + tiny + .cc).
If a URL with missing protocol is submitted in a browser address bar the http:// is automatically assumed. But when creating links in html you can't get away with dropping the protocol.
Redirects
A short URL is not a web page on its own. Instead it is simply a pointer that forwards traffic to a different address. Effectively making the same web page available under more than one address - both the original (long address) and the Tiny address. Browsers and servers talk back and forth using "headers" which contain various information. And a status code is one piece of information exchanged through a header. Let's say you click on a shortened URL ( eg. http://tiny.cc/x ). A conversation through the use of headers will take place between your computer and the tiny.cc server. Tinycc URLs use 301 redirects, which means your browser request will be responded to with a 301 = page moved permanently status code and will forward your browser to this "moved to" address (which we are calling the long URL). A search engine spider can follow links just as your browser did and is satisfied if it sees the 301 redirect method in-use. Search engines care about redirects because when they see one, they need to decide how to pass link popularity.Branded Domains
One of the biggest down sides of using a free, public URL shortener is that the same domain is shared by all users of the service and a few bad actors can lead to everyone being penalized (eg. the domain blocked by Twitter or by email services). Which means the short links you created may be treated as spam even though you personally played by the rules and never broke any terms of service.Why short links that contain custom or branded domains? If you own the domain this means no one else can abuse it. You are in complete control of the domain's reputation. On the negative side is worry about blacklisting. The positive side of custom URLs is the opportunity to build a good reputation by associating your custom domain with your business brand in the minds of your customer. And just as importantly, search engines also begin creating an association between your domain and your brand - enhancing your online presence. What does a branded domain look like?
Link Masking
Potential buyers sometimes avoid clicking if they can see that the link involves marketing efforts or affiliate commisions. Masking means that your affiliate URL never becomes visible in a browser address bar.• A very simple method if you have your own website is to create a blank html page and paste the following code into the blank page (substituting your affiliate URL).
Then name the html page something that makes sense for the application such as http://yourwebsite.com/orderpage. In this example you would use http://yourwebsite.com/orderpage in place of your affiliate URL and when clicked on, it would instantly redirect to your affiliate URL which never appears in the browser address bar before clicking.
• A second html method for website owners is to use an iframe. Instead of redirecting, an iframe loads a page within another webpage. And since the original web address never changes, the URL seen in the address bar never changes either.
• A third simple method if you don't have a website - requires only a domain name. Your domain registar account usually has URL forwarding options for the domain. So set-up URL forwarding (using a 301 redirect) to http://affiliatewebsite.com/affiliateID. This will create an instant redirect from your domain name to affiliate URL. (http://mysite.com --> http://affiliatewebsite.com/affiliateID) The customer will never see the destination URL in their browser address bar ahead of time.
There are other masking or cloaking techniques but most are frowned on by search engines due to potential for abuse and usually make use of javascript, server configuration or scripting languages such as php or perl.
Search Engines and Link Indexing
Two methods that search engines use to discover links and pages:1) Webmasters can inform search engines about new links with a submission form.
2) Search engines automatically find links when they exist on public pages.
If a link is never used on the internet or shared publicly then it doesn't exist in a cyber sense. For instance, if you have a link pointing to personal information and only you or a family member uses it, then there is no method for a web crawler to find it. It lives outside their known universe of pages and links. But be aware that even if you never intend to share a link, search engines own some web based services like Gmail, Google Drive or Google Docs (same applies to Bing and Outlook.com / OneDrive) links can be indexed, even if located inside of "private" online documents and emails.
Search engines find and index a massive amount of information, but they are not all all seeing, all knowing. See Deep Web and Dark Web. There are a lot of things that search engines never find because it's not posted on the web in a fashion that they can interpret. As another example, Google can't crawl and index the links inside of your Tinycc account. Crawlers are not allowed behind our login, and do not have a way to get into accounts. Short links are not pages on our site, they are stored in a database that robots have no general access to. So unless shared or exposed publicly, short links never appear in search results.
Short URLs and Beacons
Short URLs and beacons team up. Short URLs allow for editing (updating the destination page) as well as for implementing tracking options. Beacons are proximity marketing tools and can also be used for indoor navigation and asset tracking.• Eddystone is a beacon profile released by Google - programmable by end user to work in UID, TLM or URL mode.
• iBeacon is a protocol developed by Apple.
Beacons determine physical location, track customers, or trigger a location-based action on the device such as a check-in on social media or a push notification. Brick and mortar retail stores use beacons for mobile commerce and mobile marketing, like offering customers special deals and can even enable mobile payments through point of sale systems. Other applications include distributing messages at a specific Point of Interest:
Retail Stores
Deliver in-store notifications for special offers, campaigns or play content.
Airports & Rail Stations
Deliver alerts and notifications, send marketing content, notify schedule changes, conduct general survey.
Restaurants
Notify about upcoming events, food coupons, attract new customers, special offers for existing customers, gather feedback.
Events & Trade Fair
Deliver welcome messages, stall/venue specific information, special discounts, promotions etc.
Shopping Malls
For retail marketing, improving customer experience and engagement, run special promotions or flash sales.
Museums, Historic Sites and Tours
Deliver artifact details directly on mobile devices, promotions, surveys and welcome messages
Shortcomings of URL Shorteners